Neo4j, developed by Neo Technology, is one of the earliest and most popular graph databases in the market. Here’s a brief overview of its history:
History of Neo4j:
- Origins (2000s): The idea for Neo4j originated in 2000 when the co-founders, Emil Eifrem, Johan Svensson, and Peter Neubauer, were working on a content management system in Sweden. They found traditional relational databases ill-suited for handling complex, interconnected data.
- Official Launch (2007): Neo4j was formally launched by Neo Technology (later rebranded as Neo4j, Inc.) as the world’s first graph database. It was initially developed to provide a new way of storing and querying data, focusing on relationships between entities rather than rigid tabular structures.
- Open Source Release (2010): In 2010, Neo4j was released as an open-source project, making it accessible to a broader developer community.
- Cypher Query Language (2011): The introduction of Cypher, a declarative query language designed specifically for working with graph data, was a major milestone. Cypher made querying graph data intuitive and readable, contributing to Neo4j’s rapid growth in popularity.
- Enterprise Features and Cloud Services (2013-2017): Over the years, Neo4j expanded its capabilities with enterprise-grade features, including high availability, clustering, and enhanced security. In 2017, Neo4j Aura, a fully managed cloud service, was launched, allowing organizations to deploy Neo4j on-demand without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Graph Analytics and AI Integration (2018-2022): Neo4j continued to evolve with the introduction of graph analytics, machine learning integrations, and support for advanced AI workflows, making it a powerful tool for data scientists and researchers.
- Current Status: Today, Neo4j is widely used by enterprises across various industries, including finance, healthcare, telecommunications, and government, for applications requiring deep data relationships and real-time analytics.
Neo4j’s history reflects the growing demand for graph-based data models, which provide unparalleled insights into complex data relationships that traditional databases struggle to handle. Its open-source roots, robust enterprise features, and expanding ecosystem continue to drive its adoption globally.
Neo4j is designed to handle highly connected data, making it suitable for applications that require complex querying of relationships, such as social networks, recommendation systems, fraud detection, and network management.
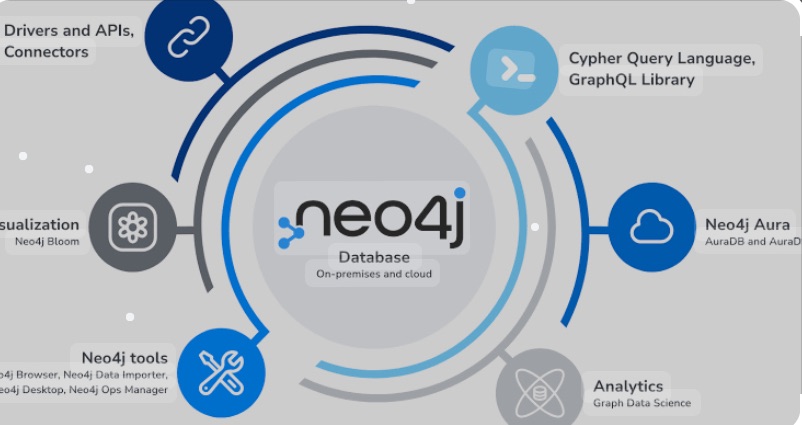
Key Features of Neo4j:
- Graph Data Model: Neo4j uses a property graph model consisting of nodes, relationships, and properties. Nodes represent entities, relationships connect nodes, and properties store data about nodes and relationships.
- Cypher Query Language: Neo4j uses Cypher, a powerful and expressive query language specifically designed for working with graph data. It allows developers to query and update data in a way that’s both intuitive and efficient.
- Scalability: Neo4j is built to scale out for both read and write operations, making it suitable for applications that need to handle large amounts of interconnected data.
- ACID Compliance: Neo4j provides strong data consistency and transaction integrity, ensuring reliable data storage and retrieval.
- High Performance: Neo4j is optimized for fast traversals, making it extremely efficient at finding connections and patterns in the data.
Common Use Cases:
- Social Networks: Representing and querying social graphs, such as users, friendships, and interactions.
- Recommendation Engines: Providing personalized recommendations based on user behavior and relationships.
- Fraud Detection: Identifying suspicious patterns and connections between entities.
- Knowledge Graphs: Storing and querying large amounts of interconnected knowledge, such as in AI and machine learning applications.
Getting Started:
To start with Neo4j, you can install it locally, use it in the cloud via Neo4j Aura, or embed it within your application. It supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, and JavaScript, through its various drivers.
Neo4j has been successfully implemented in a variety of industries, demonstrating its power in managing and analyzing complex, highly connected data. Here are some notable examples of successful implementations:
1. LinkedIn – Social Network Analysis
- Use Case: LinkedIn uses graph databases to manage its professional social network, analyzing connections between users to suggest potential job opportunities, connections, and endorsements.
- Success: By leveraging Neo4j, LinkedIn can rapidly query relationships between millions of users and deliver personalized content in real-time.
2. NASA – Knowledge Graph for Space Missions
- Use Case: NASA uses Neo4j to manage complex knowledge graphs that connect vast amounts of data related to space missions, equipment, and historical records.
- Success: The implementation enables NASA to efficiently query and visualize relationships between entities, enhancing research, and operational planning.
3. eBay – Fraud Detection and Recommendations
- Use Case: eBay uses Neo4j for fraud detection and to power its recommendation engine. By analyzing the patterns and relationships between buyers, sellers, and products, eBay can detect suspicious activities and provide personalized recommendations.
- Success: Neo4j’s graph-based approach allows eBay to uncover fraud patterns that traditional methods might miss, significantly reducing fraudulent activities on the platform.
4. UBS – Risk Management and Regulatory Compliance
- Use Case: The global financial services company UBS uses Neo4j for risk analysis, regulatory compliance, and managing complex financial relationships. Neo4j helps UBS visualize and assess interconnected risk factors more effectively.
- Success: The use of Neo4j allows UBS to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and manage risks with greater precision and speed, which is crucial in the highly regulated finance industry.
5. Microsoft – Azure Digital Twins
- Use Case: Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins, a platform for creating digital representations of physical environments, uses Neo4j to model and query complex relationships between entities in real-world systems.
- Success: This implementation allows businesses to create highly detailed, real-time models of their operations, from manufacturing to smart buildings, enhancing efficiency and decision-making.
6. Walmart – Supply Chain Optimization
- Use Case: Walmart uses Neo4j to optimize its supply chain logistics by mapping the flow of goods, identifying bottlenecks, and predicting disruptions.
- Success: The graph-based model helps Walmart improve delivery times, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency by understanding and optimizing the interconnected aspects of its supply chain.
7. Panama Papers Investigation – Data Journalism
- Use Case: The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) used Neo4j to analyze the Panama Papers, a massive dataset containing information on offshore entities and the people connected to them.
- Success: Neo4j enabled journalists to quickly identify hidden connections between offshore companies and individuals, leading to the exposure of major global financial scandals.
8. Airbnb – Knowledge Graph for Search and Discovery
- Use Case: Airbnb uses Neo4j to power its search and discovery features, enabling it to model and analyze the relationships between listings, hosts, guests, and reviews.
- Success: By leveraging Neo4j, Airbnb can provide more relevant search results and recommendations, enhancing user experience and engagement.
These examples demonstrate Neo4j’s versatility and effectiveness in handling complex, connected data across different industries, significantly improving operational efficiency, decision-making, and user experience.
Leave a comment